
Introduction
Vietnam is a captivating destination that has captured the hearts of travelers from around the world. From its breathtaking natural landscapes to its vibrant cities, Vietnam offers a unique and unforgettable experience. However, before you can embark on your Vietnamese adventure, you need to navigate the world of visas.
In this comprehensive article, we’ll dive into the intricacies of obtaining a visa to visit Vietnam, exploring the different options available and the pros and cons of each. Whether you’re considering the Vietnam e-visa or the traditional visa on arrival, we’ve got you covered. We’ll also touch on the crucial details of visa numbers, costs, requirements, and the differences between e-visas and tourist visas. Additionally, we’ll compare the e-visa and visa on arrival options for Thailand, as well as provide insights on the process of extending your Vietnam e-visa.
By the end of this article, you’ll have a deep understanding of the visa landscape in Vietnam, equipping you with the knowledge to make an informed decision and ensure a smooth and hassle-free entry into this remarkable country.
Vietnam E-Visa vs Visa on Arrival

Definition and process of obtaining Vietnam e-visa
The Vietnam e-visa is an electronic visa that allows eligible travelers to enter the country without the need for a physical visa stamp in their passport. This convenient option was introduced by the Vietnamese government in 2017 to streamline the visa application process and make it more accessible to international visitors.
To apply for a Vietnam e-visa, you’ll need to complete an online application form, submit a passport-style photograph, and make the necessary payment. The application process is relatively straightforward and can be done from the comfort of your own home. Once your application is approved, you’ll receive an e-visa document that you can present at your designated entry point in Vietnam.
Definition and process of obtaining visa on arrival in Vietnam
The traditional visa on arrival (VOA) option is another way to obtain a visa for Vietnam. As the name suggests, this method allows travelers to secure their visa upon arrival at one of the designated international airports in Vietnam. The process typically involves filling out a visa application form, submitting a passport-style photograph, and paying the required fee.
To obtain a visa on arrival, you’ll need to have a pre-approved visa letter, which you can obtain by applying through a licensed Vietnamese travel agency or a visa service provider. This pre-approval letter is then presented to the immigration authorities upon arrival, along with your passport and the necessary documents.
Pros and cons of each option
Vietnam E-Visa Pros:
- Convenient and time-saving: The online application process allows you to secure your visa from the comfort of your own home, eliminating the need to visit an embassy or consulate.
- Faster processing: E-visa applications are generally processed more quickly than traditional visa applications, often within a few business days.
- Flexibility: E-visas are valid for a single entry and a stay of up to 30 days in Vietnam.
- Wider entry points: E-visas can be used at more designated entry points, including international airports and some land border crossings.
Vietnam E-Visa Cons:
- Limited eligibility: The e-visa option is only available to citizens of specific countries, while the visa on arrival is open to a broader range of nationalities.
- Restricted entry points: E-visas can only be used at certain designated international airports and land border crossings, whereas visa on arrival can be used at a wider range of entry points.
- Higher cost: The Vietnam e-visa typically comes with a higher application fee compared to the visa on arrival option.
Visa on Arrival Pros:
- Wider eligibility: The visa on arrival option is available to a broader range of nationalities, making it accessible to more travelers.
- Lower cost: The visa on arrival fee is generally lower than the e-visa application fee.
- Flexibility: Visa on arrival can be used at a wider range of international airports in Vietnam.
Visa on Arrival Cons:
- Time-consuming process: Obtaining a visa on arrival can be a more time-consuming process, as travelers may need to wait in line at the immigration counter upon arrival.
- Pre-approval required: Travelers need to obtain a pre-approval letter before arrival, which adds an extra step to the process.
- Limited entry points: Visa on arrival can only be used at specific international airports in Vietnam, whereas e-visas have a wider range of designated entry points.
When choosing between the Vietnam e-visa and visa on arrival, it’s essential to consider your specific travel plans, the cost, and the convenience that each option offers. Factors such as your nationality, the length of your stay, and your preferred entry point can all influence the decision.
Vietnam E Visa or Visa on Arrival
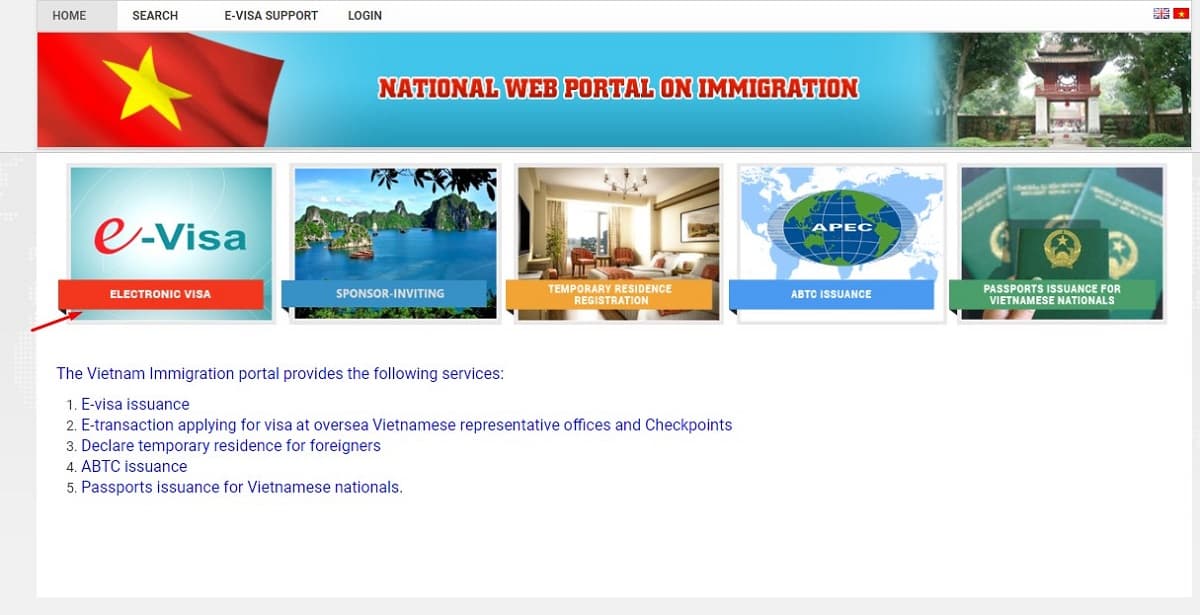
Factors to consider when choosing between e-visa and visa on arrival
When deciding between the Vietnam e-visa and visa on arrival, there are several factors to consider:
Nationality and Eligibility: The first factor to consider is your nationality and whether you’re eligible for the e-visa or visa on arrival. The e-visa option is currently available to citizens of specific countries, while the visa on arrival is open to a broader range of nationalities.
Preferred Entry Point: Another important factor is your preferred entry point into Vietnam. E-visas can be used at a wider range of designated international airports and land border crossings, while visa on arrival is limited to specific international airports.
Processing Time: The processing time is another crucial consideration. E-visa applications are generally processed more quickly, often within a few business days, while the visa on arrival process can be more time-consuming, as you’ll need to wait in line upon arrival.
Cost: The cost is also a factor to weigh. The Vietnam e-visa typically comes with a higher application fee compared to the visa on arrival option.
Travel Plans: Your travel plans, such as the length of your stay and the purpose of your visit, can also influence your decision. The e-visa and visa on arrival options may have different validity periods and restrictions.
By carefully considering these factors, you can make an informed decision on the best visa option for your specific needs and travel plans.
Visa Number in Vietnam E Visa

Importance of visa number in Vietnam e-visa application process
The visa number is a crucial piece of information in the Vietnam e-visa application process. This unique number is assigned to each e-visa upon approval and is an essential part of the documentation you’ll need to present at the immigration counter upon arrival in Vietnam.
The visa number serves several important functions:
- Verification: The visa number allows immigration authorities to quickly and easily verify the authenticity of your e-visa. This helps to streamline the entry process and ensures a smooth arrival experience.
- Tracking: The visa number can be used to track the status of your e-visa application, from the initial submission to the final approval. This can be helpful if you need to make any inquiries or follow up on your application.
- Compliance: The visa number is required to be included on various forms and documents, such as your airline ticket and arrival/departure cards. Failing to provide the correct visa number can lead to delays or even issues at the border.
- Extension: If you need to extend your e-visa during your stay in Vietnam, the visa number will be an essential piece of information required in the extension process.
Ensuring that you have the correct visa number and that it is properly documented on all your travel documents is crucial for a hassle-free entry and stay in Vietnam. It’s important to double-check your e-visa documentation to ensure that the visa number is accurate and easily accessible.
Vietnam E Visa Cost
Breakdown of costs associated with Vietnam e-visa application
The cost of a Vietnam e-visa can vary depending on several factors, such as your nationality, the processing time, and any additional services you may require. Here’s a breakdown of the typical costs associated with the Vietnam e-visa application:
Base Application Fee: The base application fee for a Vietnam e-visa is typically between $25 and $50 USD, depending on your nationality. This fee covers the processing of your application and the issuance of the e-visa document.
Expedited Processing Fee: If you need your e-visa processed more quickly, you can opt for an expedited service. This typically comes with an additional fee, which can range from $10 to $50 USD or more, depending on the desired processing time.
Service Fees: Some visa service providers or travel agencies may charge an additional service fee for assisting with the e-visa application process. These fees can vary widely, so it’s important to carefully review the terms and conditions before selecting a provider.
Conversion Fees: If you’re required to pay the e-visa fee in a currency other than USD, you may incur a conversion fee, which is typically a percentage of the total amount.
Travel Insurance: While not mandatory, some travelers choose to purchase travel insurance that includes coverage for visa-related issues, such as application delays or denials. The cost of this insurance can range from a few dollars to several hundred dollars, depending on the coverage and your travel plans.
It’s important to note that the Vietnam e-visa fee is non-refundable, even if your application is ultimately denied. Therefore, it’s crucial to ensure that you meet all the necessary requirements and provide accurate information when applying to avoid any unnecessary costs or delays.
Vietnam E Visa Requirements
List of documents and requirements for applying for Vietnam e-visa
To apply for a Vietnam e-visa, you’ll need to submit the following documents and meet the following requirements:
Passport: Your passport must be valid for at least 6 months beyond the intended date of entry into Vietnam. Additionally, your passport must have at least one blank visa page available for the e-visa stamp.
Passport Photo: You’ll need to provide a recent, passport-style photograph that meets the required specifications. This photo will be uploaded as part of your e-visa application.
Proof of Onward Travel: You’ll need to provide proof of your onward travel plans, such as a return flight ticket or a booking for a connecting flight or train.
Visa Application Form: You’ll need to complete an online visa application form, which will require personal information, travel details, and other relevant information.
Payment: The e-visa application fee must be paid online using a credit or debit card, or through other approved payment methods.
Travel Insurance (Optional): While not mandatory, some travelers choose to purchase travel insurance that includes coverage for visa-related issues.
It’s important to ensure that all the information and documents provided are accurate and up-to-date to avoid any delays or issues during the e-visa application process or upon arrival in Vietnam.
Difference Between E Visa and Tourist Visa
Contrasting features of e-visa and tourist visa for Vietnam
The key differences between the Vietnam e-visa and the traditional tourist visa are as follows:
Application Process:
- E-Visa: The application is completed entirely online, with the visa document issued electronically.
- Tourist Visa: The application is typically submitted in person at a Vietnamese embassy or consulate, or through a visa service provider.
Processing Time:
- E-Visa: The processing time is generally faster, often within a few business days.
- Tourist Visa: The processing time can be longer, sometimes taking several weeks or even months, depending on the embassy or consulate.
Entry Points:
- E-Visa: Can be used at a wider range of designated international airports and land border crossings in Vietnam.
- Tourist Visa: May be limited to specific entry points, depending on the visa type and the issuing embassy or consulate.
Validity:
- E-Visa: Typically valid for a single entry and a stay of up to 30 days in Vietnam.
- Tourist Visa: Can be issued for multiple entries and have varying validity periods, depending on the visa type.
Cost:
- E-Visa: Generally has a higher application fee compared to the tourist visa.
- Tourist Visa: The cost can vary depending on the issuing embassy or consulate and the visa type.
Extension:
- E-Visa: Can be extended by applying directly to the local immigration office in Vietnam.
- Tourist Visa: Extension options may be more limited and may require leaving the country and re-applying for a new visa.
Understanding the key differences between the Vietnam e-visa and the traditional tourist visa can help you make an informed decision on the best option for your travel plans and requirements.
Thailand E Visa vs Visa on Arrival
A comparison of e-visa and visa on arrival options for Thailand
Similar to Vietnam, Thailand also offers both e-visa and visa on arrival options for international travelers. Here’s a comparison of the two:
Thailand E-Visa:
- Eligibility: Available to citizens of select countries, including China, India, and several other Asia-Pacific nations.
- Application Process: Completed entirely online, with the e-visa document issued electronically.
- Cost: The e-visa application fee is generally higher than the visa on arrival, ranging from $30 to $60 USD.
- Processing Time: E-visa applications are typically processed within 3-5 business days.
- Entry Points: Can be used at designated international airports in Thailand.
Thailand Visa on Arrival:
- Eligibility: Available to citizens of a broader range of countries, including many European and North American nations.
- Application Process: Completed upon arrival at designated immigration counters in Thailand.
- Cost: The visa on arrival fee is typically lower than the e-visa, ranging from $30 to $45 USD.
- Processing Time: The visa on arrival process can be more time-consuming, as travelers need to wait in line upon arrival.
- Entry Points: Can be used at specific international airports in Thailand.
When choosing between the Thailand e-visa and visa on arrival, factors to consider include your nationality, the length of your stay, the cost, and your preferred entry point. The e-visa may be more convenient for some travelers, while the visa on arrival can be a more cost-effective option for others.
It’s important to note that the specific requirements and procedures for both the Thailand e-visa and visa on arrival can change over time, so it’s always a good idea to check the latest information from the Thai government or a reliable travel information source.
Vietnam E Visa Extension
Process and requirements for extending a Vietnam e-visa
If you find that you need to extend your stay in Vietnam beyond the initial 30 days granted by your e-visa, it is possible to apply for an extension. However, the process can be a bit more complex than the initial e-visa application.
Process for Extending a Vietnam E-Visa:
- Application Submission: You’ll need to submit an application for a visa extension to the local immigration office in Vietnam. This can typically be done in person or by mail, depending on the specific requirements.
- Required Documents: The required documents for a visa extension may include your passport, a completed application form, a recent passport-style photograph, and proof of your ongoing travel plans or stay in Vietnam.
- Processing Time: The processing time for a visa extension can vary, but it’s generally recommended to apply for the extension at least a few days before your existing e-visa is set to expire.
- Fees: There is a fee associated with extending a Vietnam e-visa, which can range from $25 to $50 USD or more, depending on the specific circumstances.
Requirements for Extending a Vietnam E-Visa:
- Valid Passport: Your passport must be valid for at least 6 months beyond the intended extension period.
- Sufficient Funds: You may be required to demonstrate that you have sufficient funds to support your extended stay in Vietnam.
- Proof of Ongoing Travel: You’ll need to provide evidence of your ongoing travel plans or reasons for extending your stay, such as hotel bookings or a letter from your employer.
- Absence of Violations: You must not have any history of visa violations or overstaying your welcome in Vietnam.
It’s important to note that the visa extension process can be subject to change, and the specific requirements may vary depending on the local immigration office and your individual circumstances. Therefore, it’s always a good idea to check with the relevant authorities or a reliable travel agency for the most up-to-date information.
Vietnam E Visa Entry Points
Designated entry points for travelers holding Vietnam e-visas
The Vietnam e-visa can be used at a designated set of international airports and land border crossings in the country. Here are the main entry points for travelers holding a Vietnam e-visa:
International Airports:
- Noi Bai International Airport (Hanoi)
- Tan Son Nhat International Airport (Ho Chi Minh City)
- Da Nang International Airport (Da Nang)
- Cam Ranh International Airport (Nha Trang)
- Phu Quoc International Airport (Phu Quoc Island)
- Van Don International Airport (Quang Ninh Province)
Land Border Crossings:
- Lao Cai (border with China)
- Mong Cai (border with China)
- Xa Mat (border with Cambodia)
- Tinh Bien (border with Cambodia)
- Moc Bai (border with Cambodia)
- Loc Ninh (border with Cambodia)
It’s important to note that the list of designated entry points for Vietnam e-visas is subject to change, and the specific requirements may vary depending on the entry point. Always check the latest information from the Vietnamese government or a reliable travel source before finalizing your travel plans.
Additionally, if you plan to enter Vietnam through a land border crossing, it’s essential to ensure that you have all the necessary documents and that you arrive during the designated operating hours forimmigration processing. Some land border crossings may have limited hours of operation or specific entry requirements, so it’s crucial to plan your travel accordingly.
When arriving at one of the designated international airports or land border crossings with a Vietnam e-visa, travelers will need to present their e-visa approval letter, along with their passport and any other required documentation, to the immigration authorities for entry into the country. It’s essential to have all your documents in order and be prepared for any potential questions from the immigration officers.
Overall, the Vietnam e-visa offers a convenient and efficient way for eligible travelers to visit the country for tourism, business, or other purposes. By understanding the designated entry points and ensuring that you meet all the requirements for the e-visa application process, you can enjoy a smooth and hassle-free entry into Vietnam.
Vietnam E Visa Country List
Countries eligible for applying for a Vietnam e-visa
The Vietnam e-visa is available to citizens of a select group of countries, allowing them to apply for an electronic visa online before traveling to Vietnam. While the list of eligible countries may change over time, as of the latest update, some of the countries whose citizens are eligible for a Vietnam e-visa include:
- United States
- Canada
- United Kingdom
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Germany
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Japan
- South Korea
- China
- India
- Singapore
- Malaysia
- Thailand
- Indonesia
- Philippines
This is not an exhaustive list, and there may be additional countries whose citizens are eligible for the Vietnam e-visa. It’s essential to check the latest information from the Vietnamese government or the official e-visa application website to confirm your eligibility based on your nationality.
For citizens of countries not included in the Vietnam e-visa eligibility list, alternative visa options, such as visa on arrival or traditional embassy visas, may be available. It’s recommended to explore all visa options and choose the one that best suits your travel plans and requirements when visiting Vietnam.
E-Visa Vietnam Application
Step-by-step guide on how to apply for an e-visa for Vietnam
Applying for an e-visa for Vietnam is a straightforward process that can be completed entirely online. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to apply for a Vietnam e-visa:
Step 1: Access the Official E-Visa Website Visit the official Vietnam e-visa application website to start the application process. Make sure you are on the correct website to avoid any potential scams or fraudulent activities.
Step 2: Fill Out the Application Form Complete the online application form with accurate and up-to-date information. You will need to provide details such as your personal information, passport details, travel itinerary, and contact information.
Step 3: Upload Required Documents Upload scanned copies of the required documents, including your passport bio page and a recent passport-style photograph. Ensure that the documents meet the specified format and size requirements.
Step 4: Pay the Application Fee Pay the e-visa application fee using a valid credit or debit card. The fee amount may vary depending on your nationality and the type of visa you are applying for.
Step 5: Wait for Processing After submitting your application and payment, wait for the processing of your e-visa. The processing time is typically around 3-5 business days, but it may vary depending on the volume of applications.
Step 6: Receive and Print Your E-Visa Once your e-visa is approved, you will receive an electronic copy of the visa approval letter via email. Download and print this document to present to the immigration authorities upon arrival in Vietnam.
By following these steps and ensuring that you provide accurate information and required documents, you can successfully apply for a Vietnam e-visa and enjoy a seamless entry into the country for your travels.
Notes
Additional information and tips for a smooth visa application process
When applying for a Vietnam e-visa or any other type of visa, there are several additional tips and considerations to keep in mind to ensure a smooth application process:
Check Eligibility: Before starting your visa application, verify that you meet all the eligibility criteria for the specific visa type you are applying for. Make sure your nationality is eligible for the e-visa or visa on arrival option.
Plan Ahead: It’s advisable to apply for your visa well in advance of your planned travel dates to allow for any processing delays or unforeseen issues. Avoid last-minute applications to prevent any travel disruptions.
Double-Check Documents: Review all the required documents and information before submitting your visa application. Ensure that your passport is valid for the required period, and all uploaded documents meet the specified criteria.
Follow Instructions: Pay close attention to the instructions provided on the visa application website and follow them carefully. Any errors or omissions in the application may lead to delays or rejection of your visa.
Stay Informed: Keep yourself updated on any changes to visa regulations or requirements for your destination country. Check for any travel advisories or updates that may impact your visa application or travel plans.
By staying informed, planning ahead, and following the guidelines provided for the visa application process, you can increase your chances of a successful visa approval and enjoy a hassle-free journey to Vietnam or any other destination.
Mistakes to Avoid
Common errors to steer clear of when applying for a Vietnam e-visa
When applying for a Vietnam e-visa, it’s essential to avoid common mistakes that could lead to delays or rejection of your visa application. Here are some common errors to steer clear of during the e-visa application process:
Providing Inaccurate Information: One of the most critical mistakes to avoid is providing incorrect or inaccurate information on your visa application. Double-check all details, including passport numbers, travel dates, and personal information, to ensure accuracy.
Uploading Incorrect Documents: Ensure that you upload the correct documents in the specified format and size as required by the e-visa application guidelines. Uploading blurry, incomplete, or incorrect documents can lead to application rejections.
Missing Application Deadlines: Missing the application deadlines or submitting your e-visa application too close to your travel dates can result in processing delays or insufficient time to rectify any issues with your application.
Neglecting Passport Validity: Make sure that your passport is valid for at least six months beyond your intended stay in Vietnam. An expired passport can lead to visa application rejection or entry denial upon arrival.
Ignoring Updates or Changes: Stay informed about any updates or changes to the visa application process or requirements. Ignoring important notifications or failing to adapt to new guidelines can result in application errors.
By avoiding these common mistakes and taking the necessary precautions during the Vietnam e-visa application process, you can enhance your chances of a successful visa approval and enjoy a stress-free travel experience to Vietnam.
Frequently Asked Questions
Answers to commonly asked queries about Vietnam e-visas and visa on arrival
Q: How long is the validity of a Vietnam e-visa? A: A Vietnam e-visa is typically valid for a single entry and allows for a stay of up to 30 days in the country. The validity period starts from the date of entry specified in your visa approval letter.
Q: Can I extend my stay in Vietnam with an e-visa? A: Yes, it is possible to apply for a visa extension if you need to prolong your stay in Vietnam beyond the initial 30 days granted by your e-visa. The extension process involves submitting an application to the local immigration office.
Q: Is a visa on arrival the same as a Vietnam e-visa? A: No, a visa on arrival and a Vietnam e-visa are two different types of visas. A visa on arrival is obtained upon arrival at designated immigration counters in Vietnam, while an e-visa is applied for and approved online before travel.
Q: Can I enter Vietnam through any border crossing with an e-visa? A: No, the Vietnam e-visa can only be used at designated international airports and land border crossings in the country. It’s essential to check the list of entry points for e-visa holders before planning your travel.
Q: How far in advance should I apply for a Vietnam e-visa? A: It’s recommended to apply for a Vietnam e-visa at least a few weeks before your intended travel dates to allow for processing time and any potential delays. Avoid last-minute applications to ensure a smooth travel experience.
By addressing these frequently asked questions and providing clarity on common concerns related to Vietnam e-visas and visa on arrival, travelers can better understand the visa options available and make informed decisions for their upcoming trips.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice between a Vietnam e-visa and visa on arrival depends on various factors such as eligibility, cost, processing time, and convenience. Both options offer advantages and limitations, so travelers should consider their individual preferences and travel plans when selecting the most suitable visa type.
The Vietnam e-visa provides a convenient and efficient way for eligible travelers to obtain a visa online before arriving in the country, while the visa on arrival offers flexibility for a broader range of nationalities. Understanding the requirements and procedures for each visa type is essential to ensure a smooth entry into Vietnam.
Additionally, the process of extending a Vietnam e-visa, knowing the designated entry points, and checking the list of eligible countries are crucial aspects to consider when planning a trip to Vietnam. By following the guidelines, tips, and recommendations outlined in this article, travelers can navigate the visa application process with confidence and ease.
Whether you choose a Vietnam e-visa or visa on arrival, proper preparation, attention to detail, and adherence to the visa requirements are key to a successful travel experience. Stay informed, plan ahead, and enjoy your journey to Vietnam, exploring its rich culture, history, and natural beauty with peace of mind.

Leave a Reply